International Master Program in Perinatal Medicine

The ‘International Master Program in Perinatal Medicine’ offers advanced education in perinatal care for the unborn baby and the mother to be. The training consists of a theoretical-practical part and interactions part in person in Istanbul.
The theoretical-practical part will be as an online training with specific modules for basic and advanced level of knowledge together with practical tasks such as discussing clinical cases and submitting images to validate the acquisition of the necessary skills. This part is supported by an interactive platform consisting of discussion forums and masterclasses given by experts in the field.
The Interaction part of this training is in person training and 3 face-to-face weeks in Istanbul. During these weeks there will be meet-the-professor sessions, practical workshops on invasive procedures and clinical cases discussions. (You can see forther details in the training guide).
Contents
-Pre-registration and selection criteria
-MODULE-2: Fetal morphologic and genetic diagnosis
-MODULE-3: Doppler and placental pathology
-MODULE-4: Fetal echocardiography
-MODULE-5: Fetal neurosonography
-Online exams of the theoretical modules
Targeted trainees
 Specialists in Obstetrics and Gynaecology, with at least a 2-year dedication background on perinatal medicine*
Specialists in Obstetrics and Gynaecology, with at least a 2-year dedication background on perinatal medicine*
*The academic syllabus of the master program includes topics not directly related to imaging technically.
Objective
Trainess will receive high-level training in all relevant aspects for the practice of perinatal medicine in provided by sub-specialists with experience in clinical practice, training and research.
To acquire theoretical and practical knowledge in the different perinatal medicine fields, such as:
* Maternal and obstetric disorders
* Placental disorders
* Fetal anomalies
* Obstetric examination
* Advanced fetal examination
* Fetal diagnosis
To provide a forum to have experiences and knowledge with sub-specialists and experts.
To promote the debate and critical care about new advances in the perinatal medicine.
To practice the knowledge in a practical high-quality advanced simulation model.
To get the skills to perfom a systematic assessment in the different aspects of perinatal medicine (prenatal diagnosis, echocardiography, neurosonography…)
Training structure
The training program of the International Master in Perinatal Medicine includes six theoretical modules together with practical aspects in perinatal medicine and advanced training through theoretical classes and an interactive platform, online practical training through image acquisition.
Each module will have a certain duration and be carried out sequentially as outlined below.
Online theoretical part includes several online classes, given by specialists in perinatal medicine with also the expert discussion of clinical cases, and the masterclass given by the tutor of each module allows an opportunity the interaction between the trainees and the tutors with the aim of solving all the doubts that may arise during the modules.
Once the theoretical part described above is completed, the online practice-at-home part begins, which will consist of obtaining and submitting a certain number of images with defined criteria set in theoretical part. These images will be evaluated and scored by the course tutors and the trainees will receive a personalized feedback that will allow them to detect potential pitfalls in order to improve their practice. This is intended to improve his/her performance in fetal examination in their daily practice. Some modules also require the submission of documented clinical cases together with the images.
Finally, as an evaluation purposes, every module has an exam that must be passed separately to obtain the title of the International Master in Perinatal Medicine.
The last module consists of a research project which will be evaluated by the Committee of Experts. For the research project, the trainee will be assigned to a tutor who will supervise and guide him/her to complete the final work.
Here, you can see the program and the contents and the coordinators
Training structure
The training program includes six modules covering all relevant aspects for the practice of perinatal medicine. Each module is for 6-8 weeks.
Online training modules and evaluation tests
Each module contains the theoretical contents that can be seen online. These modules have a determined duration and will be carried out consecutively. Whenever a module is completed, there will be an evaluation test by multiple-choice questions that can include images and videos for a specific deadlines of completion.
Masterclasses
The Masterclasses are interactive sessions with the professors that will be scheduled in the form of live online webinars, in which the trainees will ask their questions to the experts, for solving any doubts that may have remained. These sessions will be held before the end of the online exam period of each module, and they will be coordinated by a moderator to ensure that they run smoothly.
Quality control of the master program
For each module, a set of examination images must be obtained and sent in electronic format. Images must be obtained according to pre-established criteria for the acquisition, quality and magnitude.
The images will be assessed and scored by the tutors of the training; the trainees will receive a personalized feedback that will allow them to detect possible pitfalls in order to improve their clinical skills.
The objective of this part is to provide decision making and problem-solving skills in fetal examination that are essential in the doctor’s daily clinical practice.
Clinic cases resolution
A forum will be created for each module using the moodle platform. The trainees will be given access once the module is open for the opportunity to share questions and doubts regarding the relevant topics. The directors of the module will propose clinical cases to generate a debate between the trainees.
Training in person (Face-to-face) Week
From June 5 to June 20, 2023
From November 5 to November 20, 2023
From March 5 to March 20, 2024
From August 15 to August 30, 2024
The face-to-face part includes a 8-weeks period in Istanbul, that consists in:
- Meet-the-Professor sessions, in which the trainees will be able to discuss in person the most relevant aspects of each module with the professors.
- Practical workshops on invasive procedures, with the guidance of the experts in these procedures.
- Clinical cases sessions, in groups of 10-12 participants, where some examples of real clinical cases will be discussed to put the knowledge acquired in the different modules into practice. Trainees will be asked to present their own clinical cases and will be discussed within the group with the supervision of an expert.
Research project
The Trainees should elaborate a final research project that will be evaluated by the expert committee. There are two modalities of final project to choose: Systematic review of the literature on a current subject related to the content of the course and original research in the trainee’s own setting.
The topic of the final project must be proposed by each trainee. The proposals must be sent to the coordinator by Januray 1st, 2023 in order to be assessed by the scientific committee, which will evaluate their suitability.
The scientific committee will establish the definitive topic for each trainee’s project and assign a tutor to guide the trainee during the project. It is necessary to get the final project assessment (the passing score is 70) to obtain the university degree
Course duration
From April 15, 2023 to October 30, 2024.
Organized by
Perinatal Medicine Foundation
Course directors

Cihat Sen
Cecilia Villalain
Scientific committee
Nicola Volpe, Italy
Valentina De Robertis, Italy
Murat Yayla, Turkey
Oluş Api, Turkey
Resul Arısoy, Turkey
Gurur Biliciler-Denktas, USA
Asma Khalil, UK
Satoshi Kusuda, Japan
QiuYan Pei, China
Jun Yoshimatsu, Japan
Barış Ata, Turkey
Secreteriat
Yasemin Guzel
WhatsApp +90 542 4428736
Venue
Istanbul
Registration fees
10.000,00 €
Payment
- Once the application is accepted, a payment of 5000 € must be made soon after.
- The second payment of 5000 € will be made March, 2023.
Pre-registration and selection criteria
The number of trainess to be accepted is limited. To apply, it is necessary to fill out the pre-registration form within the established period. The form will be available from January 2023 to April 2023. Applications submitted after the deadline will not be accepted.
Pre-registration requirements:
- To be a medical doctor.
- To fill in the pre-registration form with the requested information, the CV and a reference letter.
- To send to the e-mail: [email protected]
- Your application will be confirmed within a maximum of one week from the date of submission.
Note that incomplete applications will not be considered.
Selection results
From April 2023, selected applicants will receive an email indicating that they have been accepted with the necessary information to start the registration process.
- We recommend you to read necessary information available on our website in the relevant section.
- Applicants not admitted will receive an email indicating that their application has not been accepted but could be applied for next term when available.
- Pre-registration requires a commitment to accomplish the planned educational activities to pass the training including the evaluations and the submission of images and clinical cases in each module within the established deadlines. Thus, we request that you do not submit your pre-registration application if you are not sure that you can accomplish the training requirements, either because you are not able to attend the training in person part, or meet the deadlines for the submission of images, exams, payments, etc.
Cancellations
In the case of abandoning the training program, the applicant must present a letter to the course coordinator, requesting the cancellation of his/her registration. The registration fee will not be refunded.
Training Certificate
- A diploma that certifies the completion of the “International Master in Perinatal Medicine ” will be issued by Perinatal Medicine Foundation and with a qualification certificate. To obtain the course certificate, it is essential to pass all the theoretical and the practical parts of each module.
- After satisfactory completion of all tests and materials required, participants will be provided with a university Diploma. It is a university-specific master’s degree* awarded by the Institute…. at the University of………. The name of the diploma awarded by the University will be: “Master’s degree in Perinatal Medicine” and it has …….. credits.
INFORMATION ABOUT THE UNIVERSITY DIPLOMA
What is a university-specific qualification?
- According to the regulations of the European Higher Education Area (EHEA) most European universities offer specific degrees. In Turkey, pursuant to article number… of the Law on YÖK [date and number the government allows Turkish universities to independently issue university-specific diplomas and qualifications. This enables the University to add to the official training it offers these so-called university-specific qualifications.
- University-specific qualifications are specialised courses with various names (master’s degree, postgraduate, expert, etc.). They are designed to flexibly meet the needs that arise in the labour market and society, so they are aimed at achieving objectives such as:
- Providing specialised training with an immediate impact in the professional world.
- Updating professional knowledge in order to encourage skills-building for professional practice.
- Making a connection between academic work and social reality (this objective is supported by the frequent organisation of qualifications that are taught through an agreement with public institutions and private companies).
- Therefore, the Master degree in Perinatal Medicine is an official University-specific degree issued by the University of …………….. through its institute for continuous education. This degree certifies that the participant has received specialized training in perinatal medicine.
What is the difference between university-specific qualifications and official qualifications from universities?
- The main difference between the two is that official qualifications require a series of procedures and assessments by different public bodies such as the National Agency for the Assessment of Quality and Accreditation (ANECA), which are necessary in order to do a PhD, while University-specific qualifications do not need to be validated by institutions such as ANECA.
What validity does a university-specific qualification have outside of Turkey?
- A university-specific course has the same validity inside or outside of Turkey, as it is a curricular qualification for unregulated studies approved by university boards under the Organic Law on Universities, which accredits the trainee’s continuing education.
- The European Credit Transfer and Accumulation System (ECTS) qualifies a program as a master’s degree when the required workload to achieve the learning objectives is >60 ECTS.
- The ECTS credits are used by and accepted by effectively all European universities and also by many other institutions around the world.
What is is not a university-specific master degree
- It is not a preliminary stage to access a PhD program. Under special circumstances the master could be used for these purposes according to each country’s legislation, but this is not its primary purpose. This master requires completion of a research work, with the main aim of acquiring competences in the interpretation of research literature. In some individual cases, this work may be an original research, and even trigger a publication or the continuation of a research career after the Master is completed. However, this is not the main aim of the International Master in Perinatal Medicine, and therefore it should not be considered a formal training in perinatal medicine research.
- This Master degrees does not enable professional exercise irrespective of the local regulations of each country. For this reason, only specialists in Obstetrics & Gynecology can be accepted. in some specific countries, this type of activity could be used later to accredit or obtain an additional national qualification in the field of Perinatal Medicine, but this will always depend on local regulations and it is not an automatic feature of this degree whatsoever.
Before pre-registration
- In order to validate a degree certificate awarded by a university or centre of higher education abroad, it is necessary to carry out specific procedures to verify the existence of the institution that issued the degree and the studies that have been completed, with the legalization of foreign documents.
- Information on the legalization procedure should be obtained from the university at which the course of study was completed, consular services in the country of issue, or the competent authority in each case. For more information also access the webpage of the University of ……..: link
- Establishing a connection between the academic activity and the social reality (this objective is endorsed by the organization of these degrees through agreements between public institutions and private companies).
Scientific Programme
MODULE-1: Maternal pathology
Academic Tutors:
- Cecilia Villalain Email:
- Murat Yayla – Email:
- Resul Arısoy – Email:
Masterclass by Cihat Sen
Chronic viral infections:
Hepatitis B and C, HIV(implications from conception to delivery), invasive procedures in chronic viral infection
Emerging infections in our population
Syphilis and pregnancy, Listeria and pregnancy, Zika virus, Toxoplasmosis, Varicella and simple herpes, CMV infections for diagnosis and clinical management, management of pregnancy with contac with infection diseases, vaccines
Maternal fetal pathology
Early screening of prematurity, premature rupture of membranes (PROM), risk of preterm delivery, Preeclampsia (management of maternal complications), update in gestational diabetes, thromboembolic prophylaxis, systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome, pregnancy and heart disease, thyroid diseases in pregnancy, previous c-section with obstetric implications
MODULE-2: Fetal morphologic and genetic diagnosis
Academic Tutors:
- Cihat Sen
- Mar Gil
- Petya Chaveeva
Masterclass by Cihat Sen
Morphological ultrasound
First trimester anatomical evaluation, first trimester screening, systematic morphological evaluation, basic and advanced evaluation: doppler and M mode, CNS anomalies, facial defects, congenital heart defects, lung anomalies, gastrointestinal and abdominal wall, kidneys and urinary tract anomalies, extremities anomalies and most frequent skeletal dysplasia
Screening of chromosomal and genetic anomalies
Screening for chromosomal/genetic anomalies, screening and prenatal diagnosis in multiple gestations, chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and amniocentesis, karyotyping, microarray, EXOM
MODULE-3: Doppler and placental pathology
Academic Tutors:
- Cihat Sen – Email:
- Alireza Shmashirsaz – Email:
- Nicola Volpe – Email:
Masterclass by Cihat Sen
Fetal-Placental doppler
Basics of doppler, umbilical artery, uterine artery, cerebral circulation, aortic isthmus, venous vessels
Early onset disease
Prediction and prevention of preeclampsia, management of fetal growth restriction, management of early preeclampsia, management of early fetal growth restriction
Late onset disease
Prediction and diagnosis of late fetal growth restriction, late onset fetal growth restriction, late onset preeclampsia, second trimester intrauterine growth restriction
MODULE-4: Fetal echocardiography
Academic Tutors:
- Cihat Sen – Email:
- Vaşentina De Robertis – Email:
- Christoph Berg – Email:
- Paolo Volpe – Email:
Masterclass by Cihat Sen
Introduction
Importance and epidemiology of congenital heart disease, fetal echocardiography, techniques for the measurement of fetal cardiac function
Septal congenital heart diseases
Ventricular septal defect, atrioventricular septal defect, double inlet single ventricle
Left congenital heart diseases
Left hypoplastic heart and mitral atresia, aortic stenosis/atresia, coarctation of aorta, interrupted aortic arch, other aortic arch anomalies
Right congenital heart diseases
Tricuspid atresia, Ebstein anomaly, tricuspid valve dysplasia, pulmonary stenosis-atresia
Conotruncal congenital heart diseases
Tetralogy of Fallot, transposition of great arteries, “Corrected” transposition of great arteries, double outlet right ventricle, tTruncus arteriosus
Other defects
Anomalies of pulmonary and systemic venous return, isomerisms, cardiomyopathies, tumors, intracardiac echogenic focus, asymmetry, cardiac axis deviation, tricuspid regurgitation, pericardial effusion, arrhythmias, Fetal therapy-cardiac intervention
MODULE-5: Fetal Neurosonography
Academic Tutors:
- Cihat Sen – Email:
- Valentina De Robertis – Email:
- Roee Birnbaum – Email:
- Paolo Volpe – Email:
Masterclass by Cihat Sen
Fetal neuro-anatomy
CNS anatomy and development, systematic neurosonography, MRI in the evaluation of the fetal CNS
CNS Structural anomalies
- First trimester detectable anomalies, ventriculomegaly, midline anomalies, posterior fossa anomalies, vascular anomalies, space occupying lesions, malformation of cortical development, surgical pathology: spina bifida
Acquired anomalies
- Destructive lesions of the fetal CNS, infections, prenatal fetal brain remodelling
MODULE-6: Fetal pathology
Academic Tutors:
- Cihat Sen – Email:
- Nicola Volpe – Email:
- Resul Arısoy – Email:
Masterclass by Cihat Sen
Anomalies suitable for postnatal surgery
Pulmonary anomalies: Congenital bronchopulmonary malformations, abdominal wall defects, gastrointestinal anomalies, urologic anomalies, fetal tumors, EXIT surgery
Anomalies suitable for fetal therapy
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia, hydrothorax, low urinary tract obstruction or dilation (LUTO), fetal anemia, intrauterine transfusion., alloimmune thrombocytopenia.
Pathology of multiple gestation
Early assessment in twins and selective feticide, multifetal pregnancy: triplets/more management and discordant anomaly, monochorionic twin pregnancy: TOPs, sIUGR, TRAP, TAPS
Complementary tools
Clinical cases discussions
A virtual forum will be created for each module using the Moodle platform. The forum will be supervised by the webmaster, who will ensure its correct use and functionality.
The trainees will be given access once the module is open and it will represent the place to share questions and doubts regarding the studied topics. Furthermore, the directors of the module will propose clinical cases to generate a debate between the trainees.
RULES FOR THE USE OF THE FORUM
The forum is a communication tool within the online system. The participation is subject to basic rules:
- It is expected from the trainees to be up to date on the messages and try to answer their colleagues’ questions, even though there will be a trainer that will be present as a moderator and may intervene if no trainee can help with a question.
- Before asking a question, we recommend making sure that the topic is appropriate to the specific discussion forum and that the same question has not been asked before; if this happens, the repeated question will be deleted by the webmaster.
- We recommend that new messages should be short, concise and self-explanatory.
- No administrative or technical related questions should be asked in the forums (for example: I can’t watch the videos; I can’t download the presentations…). These messages will be deleted.
- We will try to answer the questions within the period of open forum. Those questions that remain pending will be discussed in the following masterclass.
- The messages in a specific forum must match the subjects related to that forum. Any misplaced question will be deleted to keep the forums organized.
- To answer a question or reply on a topic, the post must be open first and then the Reply link or button must be clicked on
Masterclasses
At the end of each theoretical module, there will be a Masterclass given by the director/coordinator of each module, with the aim of deepen the topics of greatest interest and reinforcing the knowledge acquired from the theoretical classes.
These sessions will be held in a webinar format and the trainees will be able to solve their doubts with the experts online. The trainees can send their questions in advance to the scientific coordinator who will coordinate the sessions.
Masterclasses will be scheduled in advance and the date and time will be announced on the WEB
PRACTICE AT HOME
All the modules include a practical part that consists of obtaining and submitting a certain number of ultrasound images* that must meet the criteria explained in the theoretical classes (See the list in the ‘Practice requirements’).
General guidelines
- Images from 5 different patients should be submitted for every required image in each module. All the images for each module must be uploaded in a single PDF document. Images from the same patient can be used in different modules. For example, images from the morphology scan (Module 1) and Doppler images of the uterine arteries in the second trimester (Module 2) can be acquired from the same patient. It’s not necessary to obtain the whole set of images of each module from the same patient.
- The evaluation criteria are those defined in the algorithms for interpreting the images described in the theoretical part of the course.
- To obtain accreditation, at least 70% of the images must meet at least 70% of the defined criteria.
- The images will be uploaded for each module in the TASKS SUBMISSION section in the WEB.
- The images must be submitted in a single PDF document, displayed in the requested order for each module. The document’s size must not exceed 25 MB.
6. In order to preserve the confidentiality of the patients, the submitted images must NOT show patient names or any identity related data.
Practice submission deadlines: The calendar will be available on the WEB. If there are any changes in the deadlines for any reason, it will be announced in the campus calendar.
For each module, a set of ultrasound images must be obtained by the participant and sent in an electronic format through her/his personal interactive platform. Images must be obtained according to pre-established criteria for the acquisition, quality and magnification, and include virtually all common ultrasound exams conducted in the practice of advanced perinatal medicine.
- MODULE 1: First and second trimester anatomical standard sections and US markers.
- MODULE 2: Doppler images of the most common vessels and fetal weight estimates.
- MODULE 3: Fetal brain structures in all relevant sections.
- MODULE 4: Cervical length images in different clinical scenarios.
- MODULE 5: Cardiac structures and Dopplers in in all relevant sections.
- MODULE 6: Relevant images of a minimal number of well-documented anomalies.
RESEARCH PROJECT
This is expected to be a piece of research, either a study using their own data or a systematic review on a given topic of interest.
The specific topic for each participant will be agreed upon with one expert, who will act as supervisor and evaluator on completion of the work. Participants can obviously ask and receive advice for completing the research work, but they are expected to produce it mostly on their own.
There are two modalities to choose from on the type of the final project:
- SYSTEMATIC REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE ON A CURRENT SUBJECT RELATED TO THE CONTENT OF THE
- ORIGINAL RESEARCH IN THE TRAINEE’S OWN SETTING
The topic of the final project must be proposed by each trainee.
The proposals must be sent to the coordinator team ([email protected] ) before June 30, 2023 in order to be assessed by the scientific committee, which will evaluate their suitability.
The scientific committee will establish the definitive topic for each trainee’s project and assign a tutor to guide the trainee during the project’s development. It is necessary to pass the final work assessment (the passing score is 70) to obtain the university degree.
Presentation & format
 DEADLINE AND SUBMISSION
DEADLINE AND SUBMISSION
METHOD: The deadline for the project’s submission will be during the last practical module in March, 2023. The project must be submitted through the virtual campus in a PDF format. A specific “TASK SUBMISSION” will be enabled to upload it. Failure to submit it within the prescribed time limit means suspending the task. In case of requesting deferment of delivery, for any good reason, 2 points (about 100) will be deducted, for each day of delay in delivery.
FORMAT: The text must be formatted with 1.5 line spacing, Arial font, size 12.
a)Margins: The margins must be set to: Upper: 2 cm. Lower: 2 cm. Left: 4 cm. Right: 2 cm
b)Page numbering: Starting with the introduction, all pages must be numbered on the top-right side.
c)Tables: They must be clear, numbered with Arabic numerals in relative order, titled clearly stating their content, be self-explanatory and avoid duplicating content in the text.
GRAPHS: They must be clear, numbered with Arabic numerals in relative order, titled clearly stating their content, be self-explanatory and avoid duplicating content in the text or tables.
FIGURES: They must be numbered with Arabic numerals in a relative order and have a short title. If the image or the photo has been published previously, the origin must be mentioned in the title with appropriate citation of the reference
Guidelines for the development of the research project
ORIGINAL RESEARCH MODALITY
1)SUMMARY
It must be written in English. It must demonstrate in a concise way the hypothesis and the obtained results. The abstract must have a maximum of 350 words and be written in a structured format including the following parts:
- Introduction: Define the problem and the aim of the
- Materials and methods: Describe how the project was
- Results: Describe briefly the main results of the
- Conclusions: Report the main findings of the results and the clinical implications, if
2.THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
This section contextualizes the project developed within the current framework of knowledge. It must be less than 10 pages long. It must clearly establish the problem being investigated, the current knowledge about it and the motivation for further research. It must summarize the relevant previous studies carried
out on the subject and explain how this project is different from the prior. The theoretical framework must be strongly supported by recent scientific literature (preferably no older than 10 years).
3.HYPOTHESIS AND OBJECTIVES
Hypothesis:
A short affirmative sentence that could be accepted or rejected in an experimental or a clinical research.
General objective: It must start with an infinite verb (To determine…, To analyze…, To know…) and it must be written in a way that implies the steps needed to prove the proposed hypothesis.
Specific objectives: They must be numbered according to the stages of the project. They must be written as actions that, when executed consecutively, will allow the different stages of the project to be carried out, with the aim of accepting, correcting the hypothesis of the project.
4.MATERIALS AND METHODS
This section must be written in the past tense, indicating:
Type of study: experimental, descriptive, prospective, etc.
Sample: Detailed description of the study sample, how it was obtained, source, characteristics, size, etc.
Procedures: The methods and procedures must be clearly described. The measurement instruments (if any) must be included as annexes at the end of the project. If methods or techniques from other authors have been used, they must be described briefly with the citation of the corresponding reference.
It must be clearly stated how each of the specific objectives will be carried out.
If applicable, this section of the project must also include an explanation of the statistical approach used to analyze the data, as well as the software used for such purpose.
5.RESULTS
The research findings must be written in an objective and clear way, ideally following the order of the specific objectives and methodology. The data must be analyzed in tables, graphs, figures or images. Each of them must include an explanatory text. This section must not include the interpretation of the results, this will appear in the discussion section. When the research project compares original results with the results of other authors, the source of the compared data must be clearly explained. When a statistical analysis is included, the results must clearly state which variables are statistically different.
6.DISCUSSION
This section describes the meaning of the obtained results, in the context of what is known about the studied topic. The proposed hypothesis must be discussed and accepted. Emphasis should begiven to the new and important findings of the study. The research findings must be compared with previously published studies.
The limitations of the experimental methods must be discussed, as well as the possible implications for future studies. When appropriate, the clinical relevance of the results must be included.
7.CONCLUSIONS
The conclusions must be written as a series of short sentences, based directly on the obtained results and the experimental or clinical evidence of the project. Speculation from other projects must be avoided.
8.REFERENCES
Citations and references must follow Vancouver style.
9.ANNEXES AND APPENDICES
All the documents that are considered relevant for the research project must be included in this part. They should be cited in the text in the corresponding section and properly numbered.
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW MODALITY
In case of choosing a systematic review instead of a research project, it must be carried out following the international standards and guidelines for systematic reviews (PRISMA): http:// prismastatement.org/documents/ PRISMA%202009%20checklist.pdf, omitting the criteria related to the meta- analysis (which is not necessary in this modality of research). The following sections must be included:
1) INTRODUCTION
This section is to describe the current knowledge, the limitations of the current knowledge justifying the need for a systematic review and the objective of this review.
2) METHODS
The following must be described:
- Review methods (databases reviewed, years, languages, search syntax).
- Criteria for inclusion and exclusion of
- Review methods (number of evaluators, method of resolving disagreements between evaluators, selection of abstracts for review of articles in full text).
Also, if you want to undergo a quantitative meta-analysis, the following must be included:
- Data that are intended to be extracted from the included
- Statistical methods
3) RESULTS
The flow chart of the evaluated studies must be shown, whether they were excluded (with the rationale) or included in the systematic review.
In qualitative systematic reviews, a narrative description of the findings is needed. In quantitative systematic reviews (with metanalysis), the corresponding tables and figures must be included.
3) DISCUSSION
This section is to describe the meaning of the obtained results, in the context of what is known about the studied topic.
It must contain a discussion of whether the proposed hypothesis has been accepted or rejected.
Emphasis should be given to the new and important findings of the study. The study findings must be compared with previously published studies.
The limitations of the experimental methods must be discussed, as well as the possible implications for future studies.
When appropriate, the clinical relevance of the results must be included.
3) CONCLUSIONS
The conclusions must be written as a list of short statements, based directly on the results and on the experimental or clinical evidence of the study. Speculations from other studies must be avoided.
- REFERENCES
3) REFERENCES
The references must follow Vancouver style.
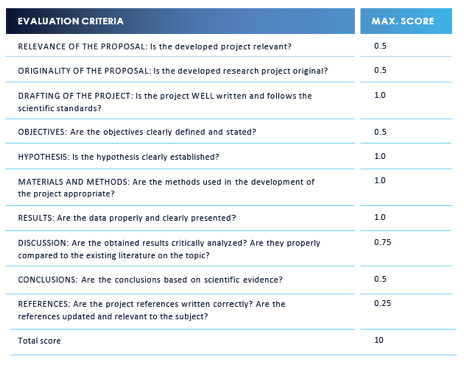
Evaluation criteria
The evaluation of the ‘Master in Perinatal Medicine’ is based on a continuous evaluation. In order to obtain the final degree, all the parts must have been passed separately.
It is imperative that trainee complete the theoretical exams, deliver the practice and participate in the forum within the agreed dates.
Failure to comply with this rule for whatever reason involves suspending the module.
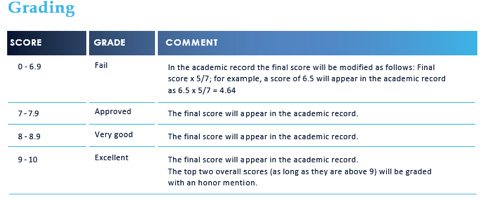
To obtain the university degree issued by University…….., it will be necessary to deliver the final project, and a minimum grade of 7 will be required for approval.
The resits of any module, practice or final work will be evaluated at a maximum 7, granting a maximum approved grade in the overall course assessment.
The non-approval of a module means the failure to obtain the course degree. The possibility of enrolling in the next year of the pending module(s) is offered, provided that the number of modules suspended is not greater than two but requires payment of the module and all corresponding university fees. In the event of suspending more than two modules there will be no option to recovery, and you would have to enroll in the Training Course again and complete it in full.
Resits: There will be only one opportunity to resit failed modules or tasks. The maximum grade that can be obtained in resits will be the minimum grade set as required to approve. This regulation does not allow exceptions of any kind.
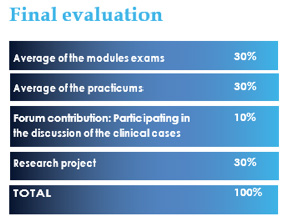
The different evaluable points of the course are described below:
ONLINE EXAMS OF THE THEORETICAL MODULES
The aim of these exams is to explore the level of knowledge acquired in relation to the content explained in the theoretical classes. They consist of multiple-choice questions test with only one valid answer per question. The different exams are composed of 50-70 questions (depending on the extension of the module).
Minimum Score: The minimum score to pass the self-assessment exams is 70%.
Duration: There is a time limit of 5 hours per exam. Time starts counting at the moment of accessing the test and continues to progress despite
disconnecting from the application. The test can be repeated 5 times with a time interval between attempts of 4 hours. Despite having passed the exam, it can be repeated up to 5 times in order to continue learning and improving the obtained score. The system will consider the best score among the 5 attempts. The average score of all the self-assessment exams
of the different modules will have an impact on the overall score of the course contributing by 45%. It is necessary to pass each module to be able to calculate the average. The exam must be carried out during the time period defined in the WEB. The time used for the submission deadlines will be Istanbul time zone (GMT +3).
PRACTICE
The images of the practice must be submitted within the requested deadlines in order to be evaluated. To obtain the final degree of the ‘Imaging in Perinatal Medicine Training Course’, this part must be passed. Any submission after the deadline will entail the non-evaluation of the practice and will be considered as failed. There will be a recovery period during the days after the ordinary deadline for each module, as explained in elsewhere.
Resits: There will be a second opportunity to resubmit any failed practice, either for not having submitted it prior to the deadline or for not having reached the necessary score to pass. The maximum score that can be obtained in the recovery will be 70%. If the trainee fails the resit, there will be no more chance of resubmission, and therefore, it will not be possible to obtain the final certificate of the ‘Imaging in Perinatal Medicine Training Course’.
Deferrals: If the trainee is unable to submit a task of a module, always before the stated date, an extension can be requested by filling out a form available on the virtual campus for consideration by the training coordinator. Extensions of deadlines will only be accepted for larger and justifiable reasons.
FORUM CONTRIBUTION, CLINICAL CASES AND MASTERCLASSES
The participation in the forum will be evaluated continuously throughout the course. Those contributions that provide answers to the questions raised in the clinical cases and the doubts generated by the rest of the participants will be positively valued. This part represents 10% of the final score.
RESEARCH PROJECT
To set the final project score,
the evaluation criteria described below will be followed. To approve the final project, a minimum grade of 7 will be required, which will count as APTO in the overall grade of the course.
FACE-TO-FACE PARTS
From June 5 to June 20, 2023
From November 5 to November 20, 2023
From March 5 to March 20, 2024
From August 15 to August 30, 2024
Professors:
Valentina De Robertis, Nicola Volpe, Paolo Volpe, Murat Yayla, Resul Arısoy, Jader Cruz, Themis Dagklis. With the participation of the course directors.
The presential part is designed to promote the contact between the course participants in addition to allowing a direct contact with the course directors and other experts in perinatal medicine in order to share their experience and vision on the integration of ultrasound in perinatal medicine and on modern perinatal medicine in general.
It consists of:
Meet the professor sessions
Sessions of 4 hours of exposure to practical aspects moderated by professors from Perinatal Medicine Foundation, with open discussions at the end of the sessions with participation of the course directors most of the days.
- Ultrasound screening.
- Fetal cardiology including echocardiography, therapy and fetal cardiac function.
- Prenatal diagnosis of chromosomic and genetic diseases.
- Brain imaging and fetal neurology.
- Placental insufficiency: IUGR and preeclampsia.
- Invasive procedures and fetal therapy.
- Twin pregnancy.
- Prematurity and PPROM.
- Fetal Infections.
- Issues around labor: labour induction, postpartum hemorrhage, fetal monitoring.
- Basics on biostatistics and research methods in fetal medicine.
- Organization of clinical and academic units and department.
Practical Sessions
During the stays in Istanbul, participants will take some simulation sessions in a state of the art facility, to train in critical obstetrical situations.
Invasive techniques workshops
The workshops will be carried out on simulators with the guidance of experts in invasive techniques for prenatal diagnosis.
Clinical Cases
Participants will be asked to present their own clinical cases and these will be discussed in a group supervised by an expert.
Principals
Cihat Sen
Director and professor
Director of Perinatal Medicine Foundation), and full Professor in Perinatal Medicine University of ……
Expert in fetal medicine and Fetal surgery,
Editor-in-Chief of Perinatal Journal
Coordinator of World School of Perinatal Medicine.
President of World Association of Perinatal Medicine
Coordinator of> 60 national and international research projects, director of 39 doctoral theses, and author of more than 485 articles with an impact factor.
Cecilia Villalain
Director and professor
Head of the Department of Fetal-Maternal Medicine at Hospital Clinic (Madrid) and Full Professor of the University of Madrid.
????????????
????????????
Coordinator
Picture and short CV
Professors
Picture and short CV
Picture and short CV
Picture and short CV
Picture and short CV
Picture and short CV

